Search Results for: atp synthase
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
ATP synthase
Definition noun, plural: ATP synthases An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of ATP from the phosphorylation of ADP with... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
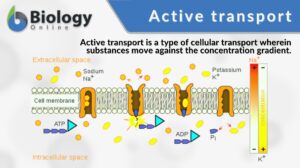
Active transport
Active transport is a type of cellular transport in which substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) are transported... Read More
Hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase
Definition noun A membrane enzyme that allows the diffusion of protons (hydrogen ions) through its proton channel component... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Chemiosmotic theory
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Brown adipose tissue
Definition noun, plural: brown adipose tissues A type of adipose tissue found in mammals that is brownish as opposed to... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Chloroplast DNA
Definition noun plural: chloroplast DNAs DNA in the chloroplast that carries the code for proteins and RNAs essential to... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Deoxyribonucleotide
Definition noun plural: deoxyribonucleotides de·ox·y·ri·bo·nu·cle·o·tide, diˌɒk... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More